Marl Hardness, Description, and Uses
Marl Hardness, Description, and Uses
Blog Article
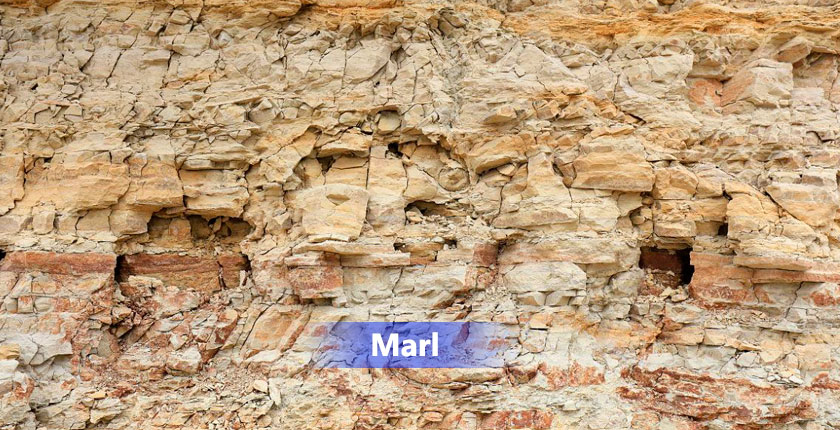

Description of marl
Marl is composed of clay particles and carbonate particles. It is a transitional type of rock between claystone and carbonate rock. Marl generally presents gray, light yellow, brown and other tones, which mainly depends on the type and content of impurities contained in it. It usually has a layered or blocky structure, with clear stratification, and sometimes horizontal or wavy textures can be seen. The hardness and density of marl are relatively low, and it is easy to cut and process.
Origin of marl
Marl is a rock formed by the mixed deposition of silt and silty mudstone. Its formation process is very complicated, involving a variety of natural factors and geological actions.
First, the main component of marl is carbonate particles, which may come from organic debris in the ocean, chemical deposition, or weathering products of altered rocks. These particles gradually deposited in the water to form the initial marl layer.
Secondly, marl also contains a large amount of silty mudstone, which is composed of fine-grained sediments such as clay and fine sand particles. These sediments are mainly derived from weathered materials, suspended material deposition and the crushing of clastic rocks. With the long-term geological evolution, these sediments gradually compacted and hardened to form a hard marl layer.

Marl Hardness
The hardness of marl is between 2-4, which is medium hardness, between limestone and claystone. The specific hardness value needs to be tested and analyzed in detail according to its composition and structure.

Physical properties of marl
Because marl contains more clay minerals, it has strong water absorption and is easy to soften in a humid environment. When subjected to external forces, marl can undergo a certain degree of plastic deformation without immediately breaking. Due to its lower hardness and higher porosity, marl is susceptible to weathering and erosion and has poor durability.
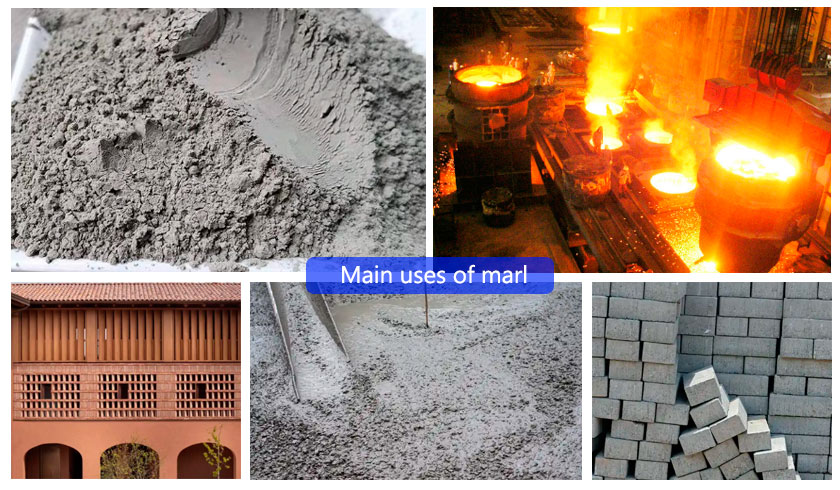

Main uses of marl
Application of marl in cement
Marl is the main raw material for burning lime and cement. By calcining marl to 1000~1300°C, quicklime (calcium oxide) can be produced, and slaked lime can be made after further processing. In cement production, marl is crushed and ground, and then put into the mill together with other materials to be ground into cement powder.
Application of marl in metallurgy
Marl can be used as a flux to help adjust the chemical composition in the furnace and promote the smooth progress of the smelting process.
Application of marl in construction
Marl can be used as a raw material for making floors, sidings, ceilings, etc. In addition, marl can also be used to make cultural stones, decorative stone carvings and decorative stones. In addition, marl can also be used to make decorations in buildings, such as vases, lamps, etc. Marl can be used as a decorative stone because of its unique color and beautiful texture, and is often used in architectural decoration and sculpture.
Application of marl in concrete
Marl can be used as an aggregate for concrete. Compared with traditional sand and gravel aggregates, marl has a higher water absorption rate and needs to control its moisture content. In addition, due to the low strength of marl, it needs to be selected and used in combination with the strength grade of concrete.
Application of marl in cement bricks
The compactness and durability of marl make it suitable for making low-strength and medium-strength cement bricks. High clay content may increase the water absorption of cement bricks, reduce their anti-penetration ability, and affect their service life. Compared with other rocks, marl has a lower hardness, which may affect the compressive strength of bricks.

What is the danger of marl?
The danger of marl is mainly reflected in its physical properties, especially the expansion after contact with water and the contraction after dehydration. This repeated expansion and contraction will cause the rock to gradually break and disintegrate. In tunnel construction, encountering marl will greatly increase the difficulty of construction. This repeated physical change makes the structure in the tunnel vulnerable to damage.
Author:[Xingaonai]
Article Title: Marl Hardness, Description, and Uses
Reprint URL: https://www.xgncrusher.com/Industralnews/Marl-Hardness-Description-and-Uses.html